As a real estate agent, you’re undoubtedly aware of the complex nature of your business. And amidst the various considerations, questions about business structures may have crossed your mind. Specifically, you may have wondered if setting up a limited liability company (LLC) is the right move for you.
In this article, we will delve into the aspects you need to consider when setting up a real estate LLC. We will also explore the pros and cons of having an LLC as a real estate agent, alternative legal structures you may want to consider, and more.
Why An LLC For Real Estate Agents?
There are two primary reasons why a real estate agent might choose to establish an LLC. The first is for legal protection, and the second is for tax advantages.
Home buyers and sellers can file lawsuits against real estate agents for various reasons, such as breach of contract, misrepresentation, or breach of duty. With high-stake transactions and strict regulations, the real estate industry is particularly susceptible to these legal challenges.
Setting up an LLC can offer you personal asset protection during lawsuits. Without a legal entity like an LLC, your personal assets may be at risk. By forming an LLC, your liability is limited to the assets in the business, shielding your personal bank accounts, property, and other assets.
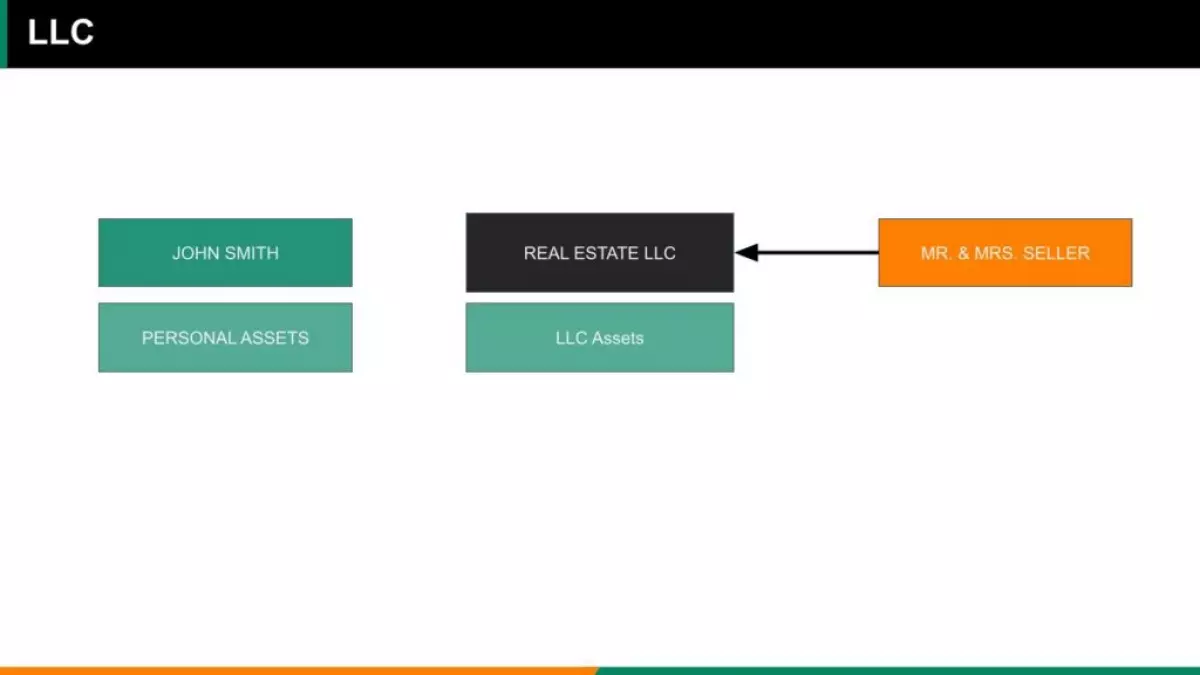 Protection of Real Estate Agent LLC
Protection of Real Estate Agent LLC
Real Estate Agent LLCs Get Tricky
However, the complexity arises when we consider the various laws and regulations surrounding real estate transactions. Real estate agents, unlike brokers, cannot directly broker real estate transactions. Contracts entered into by real estate agents are often on behalf of the broker, which complicates the liability aspects.
While establishing an LLC may offer protection, it's essential to consult with a local attorney to determine your specific liability risks and whether an LLC is the right choice for you.
Can A Real Estate Commission Be Paid To An LLC?
In most states, an unlicensed LLC cannot receive real estate commissions. A real estate agent or an individual with a broker's license must directly receive the commission. However, if you hold a broker's license, commissions can be paid to your LLC. Still, it's crucial to consider the potential implications on personal asset protection.
LLCs Offer Tax Advantages
In addition to legal protection, LLCs can provide tax flexibility and savings for real estate agents. Typically, real estate agents are considered pass-through entities, meaning profits and losses pass through to personal tax returns. However, an LLC can elect to be taxed as an S Corporation, saving a considerable amount on Social Security and Medicare taxes.
To take advantage of the tax benefits, specific requirements must be met, and proper procedures followed to avoid IRS scrutiny and penalties. It's important to note that not all real estate agents qualify for this tax strategy.
Do Real Estate Agents Need An LLC?
Determining whether an LLC is right for you depends on several factors. Here are a few scenarios where setting up an LLC typically makes sense:
- You earn enough to pay yourself a fair-market wage and generate profits.
- You have employees whom you pay.
- You are also a real estate investor.
- You have substantial personal assets you want to protect.
While the protection an LLC offers in the event of lawsuits from buyers or sellers may be subject to debate, having protection against lawsuits from employees is crucial.
Sole Proprietorship: The Alternative
If establishing an LLC is not the right path for you, you default to being considered a sole proprietor. In this case, no further action is required to establish yourself as a sole proprietor. However, if you wish to operate under a different name, you may need to file a doing-business-as (DBA) registration.
Many real estate agents opt for sole proprietorship due to its simplicity and lower costs. Unlike LLCs, sole proprietors do not have to file annual reports, making it an attractive option, especially for those starting out.
Check Insurance Options To Limit Liability
Regardless of whether you choose to form an LLC, it's important to explore insurance options to protect yourself and your assets as a real estate agent. Consider the following types of insurance:
- Errors and Omissions Insurance (E&O): This protects against common lawsuits in the real estate industry, such as errors in paperwork or failure to disclose information.
- Personal Liability or Umbrella Policy: These policies protect your personal assets in the event of damages or injury for which you may be found liable.
- Business Liability Insurance: This type of insurance provides additional coverage for your real estate business.
Best Business Structure For Real Estate Agents
The best business structure for real estate agents depends on your specific circumstances. Generally, solo agents or new agents may operate as sole proprietors, while real estate teams often choose to form LLCs. To determine the right option for you, consult with an attorney and accountant who specialize in real estate.
Want To Learn How To Set Up Your Real Estate Business?
Setting up your real estate business involves several steps, including determining your legal structure, tax classification, and banking arrangements. If you're interested in learning more about the process, we've created the "Agent Crash Course" that provides comprehensive guidance on establishing your real estate business, managing finances, and assembling a team of advisors. Start your journey today.
Remember, the information provided in this article is for entertainment and educational purposes only, and we recommend consulting with a local attorney or certified public accountant for professional advice tailored to your situation.











