Introduction
Did you know that the constellation Aries, known as the ram, has a fascinating history and mythology behind it? Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac and holds a special place in celestial mythology. In this article, we will explore the significance of Aries, its history, its prominent stars, and even its association with meteor showers and extrasolar planets. So, let's embark on a journey into the cosmos and uncover the mysteries of Aries!
Aries: The Ram Among the Stars
Aries, also known as the ram, is a constellation located in the Northern celestial hemisphere, positioned between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. In Latin, Aries means ram, and its old astronomical symbol is ♈︎. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Aries is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th in overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees.
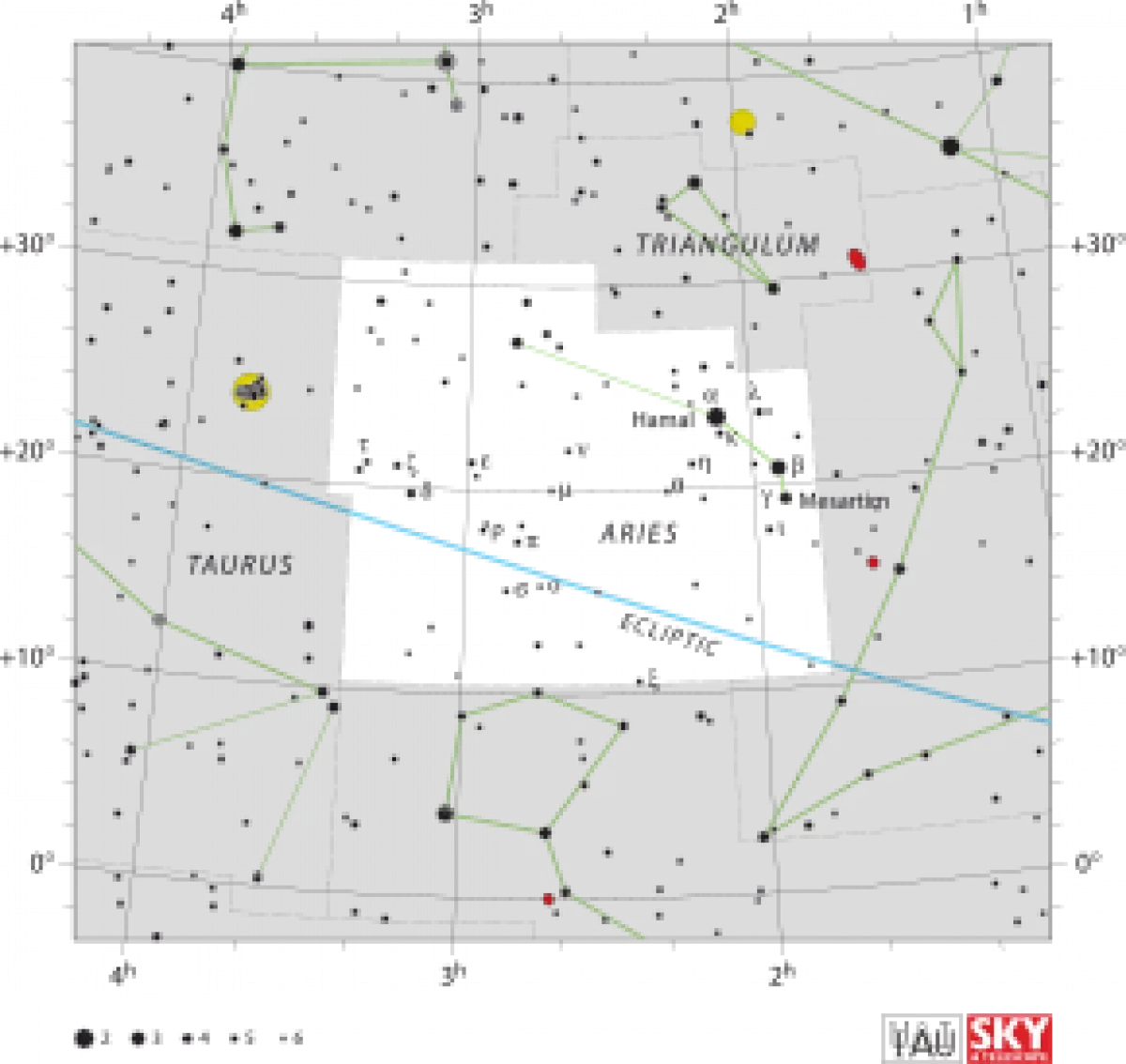 Aries (constellation)
Aries (constellation)
Throughout history, various cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations. Interestingly, Aries has not always been depicted as a ram. In late Babylonian times, the stars of Aries were seen as a farmhand. In China, they were seen as twin inspectors, and in the Marshall Islands, they were associated with a porpoise. Aries itself is relatively dim, with only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis), Sheratan (Beta Arietis), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis), and 41 Arietis.
 Aries and Musca Borealis as depicted in Urania's Mirror, a set of constellation cards published in London c. 1825
Aries and Musca Borealis as depicted in Urania's Mirror, a set of constellation cards published in London c. 1825
History and Mythology
Aries has a rich history and mythology associated with it. It was recognized as an official constellation by the International Astronomical Union and is mentioned in ancient texts as a specific pattern of stars. The constellation of Aries was seen as the final station along the ecliptic in the Babylonian zodiac. The earliest identifiable reference to Aries comes from boundary stones dating back to 1350 to 1000 BC. The shift in identification from the constellation as the Agrarian Worker to the Ram likely occurred in later Babylonian tradition due to its association with Dumuzi the Shepherd.
In ancient Egyptian astronomy, Aries was associated with the god Amun-Ra, who represented fertility and creativity. It was considered the "Indicator of the Reborn Sun" due to its location at the vernal equinox. Aries held great symbolic and mythological importance in Egyptian culture, earning the title of "Lord of the Head."
Prominent Stars in Aries
Aries is home to several prominent stars, each with its own unique characteristics. Let's explore a few of them:
-
Hamal (Alpha Arietis): Hamal is the brightest star in Aries. Its traditional name is derived from the Arabic word for "lamb" or "head of the ram" and references Aries's mythological background. It is an orange giant star with an apparent visual magnitude of 2.00.
-
Sheratan (Beta Arietis): Sheratan, meaning "the two signs" in Arabic, refers to both Beta and Gamma Arietis as heralds of the vernal equinox. It is a blue-white star and a spectroscopic binary system.
-
Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis): Mesarthim is a binary star with two white-hued components. Its traditional name has various possible origins, including a corruption of an Arabic word meaning "pair" or "fat ram." It is notable for being one of the earliest double star discoveries.
These are just a few of the stars that adorn the constellation of Aries and contribute to its celestial beauty.
Deep Sky Objects and Meteor Showers
Aries is not only home to bright stars but also to various deep sky objects and meteor showers. NGC 772 is a spiral galaxy with a prominent elliptical shape. NGC 821, on the other hand, is an elliptical galaxy displaying hints of an early spiral structure. Other notable deep sky objects include NGC 673, NGC 678, NGC 680, NGC 877, and Arp 276.
Aries also hosts several meteor showers. The Daytime Arietid meteor shower, which occurs during the day, is one of the strongest meteor showers associated with the Marsden group of comets. Other meteor showers radiating from Aries include the Delta Arietids, Autumn Arietids, Epsilon Arietids, and Sigma Arietids.
Planetary Systems in Aries
Several stars in Aries have extrasolar planets orbiting them. HIP 14810, HD 12661, HD 20367, and Teegarden's Star are just a few examples of stars in Aries with fascinating planetary systems. HIP 14810, in particular, is orbited by three giant planets, while Teegarden's Star hosts two Earth-mass exoplanets within its habitable zone.
Conclusion
Aries, the ram among the stars, has captivated astronomers and stargazers for centuries. With its rich history, mythology, and fascinating celestial features, this constellation continues to be a source of wonder and inspiration. Whether you're gazing at the bright stars of Aries or witnessing its meteor showers, there's no denying the allure of this celestial wonder. So, next time you look up at the night sky, remember to spot Aries and let its mythical presence transport you to the wonders of the cosmos.
Note: All images used in this article are from the original source.
References available upon request.











